Welcome back to the Abstract! Here are the studies this week that lurked in the dark, pulsated with light, wagged a tail, and called it a night.
First, scientists have yet again spotted a bizarre object in space that has never been seen before—the universe just keeps serving them up. Then: news from the biggest star in the sky, a tale of eavesdropping dogs, and a jellyfish sleepover.
As always, for more of my work, check out my book First Contact: The Story of Our Obsession with Aliens or subscribe to my personal newsletter the BeX Files.
You don’t want to be on this Cloud-9
Astronomers have glimpsed a new type of cosmic object—a starless clump of dark matter that never quite worked up the oomph to become a galaxy. Known as Cloud-9, the entity is located about 14 million light years away and likely provides the first look at an ancient dark matter halo.
Dark matter, as you may have heard, is weird stuff that has never been directly detected or identified, but nonetheless accounts for almost all matter in the universe. In the early universe, clumps of dark matter formed halos that attracted gas, sparked star formation, and evolved into the first galaxies. But while all galaxies appear to have dark matter halos, not all dark matter halos turned into galaxies.
Scientists have long speculated that some halos may have never accumulated the right amount of mass to make a star-studded galaxy. For years, astronomers have searched for the gravitational signatures of these dark starless “failed galaxies,” which are known as Reionization-Limited H I Clouds (RELHICs).
Now, a team reports that the first clear RELHIC candidate ever discovered, providing support for the standard model of cosmology, also known as the Lambda cold dark matter (ΛCDM) model, which is the current working framework of the universe.
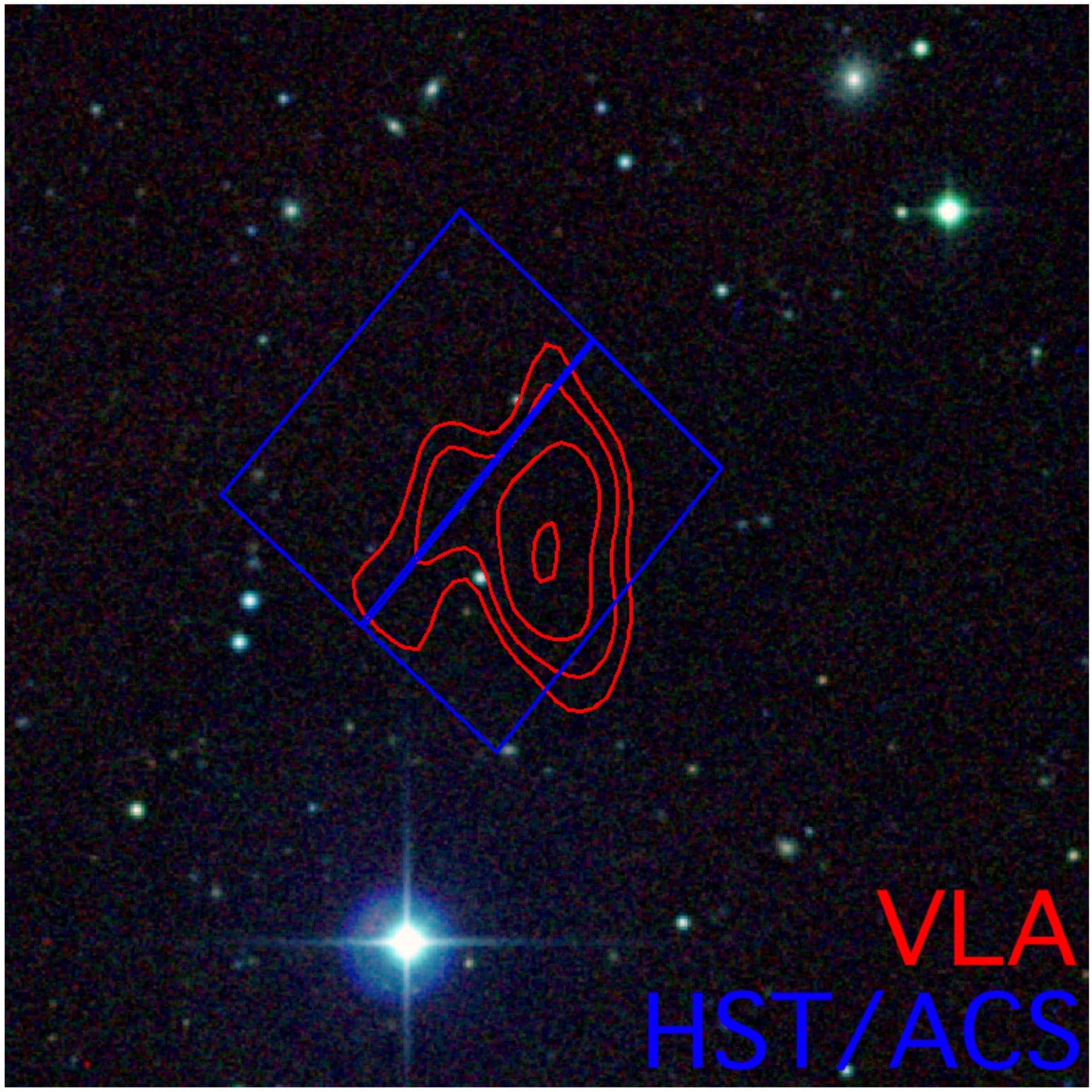
“The abundance of halos far exceeds that of known galaxies, implying that not all halos are able to host luminous galaxies,” said researchers led by Gagandeep S. Anand of the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. “This has been interpreted to mean that galaxies only form in halos that exceed a ‘critical’ mass.’”
“Our results make Cloud-9 the leading RELHIC candidate,” the team continued. “This provides strong support for a cornerstone prediction of the Lambda cold dark matter model, namely the existence of gas-filled starless dark matter halos on subgalactic mass scales, and constrains the present-day threshold halo mass for galaxy formation.”
Cloud-9 might one day accumulate enough mass to pass the threshold for star formation, allowing it to eventually graduate into a galaxy. But for now, it is a galaxy school flunkie.
In other news…
Big star go boom soon
WOH G64, one of the largest stars in the sky, is nearing its death. At about 2,000 times the size of the Sun, this supergiant would extend beyond Saturn if it were placed in our solar system.
Scientists have speculated that the recent dimming of the senescent star might signal a transition from a red supergiant to a yellow hypergiant, making it one step closer to supernova. But a new study reveals evidence that WOH G64 “is currently a red supergiant” and its changing light may be influenced by a companion star in orbit around it, making this a binary system.
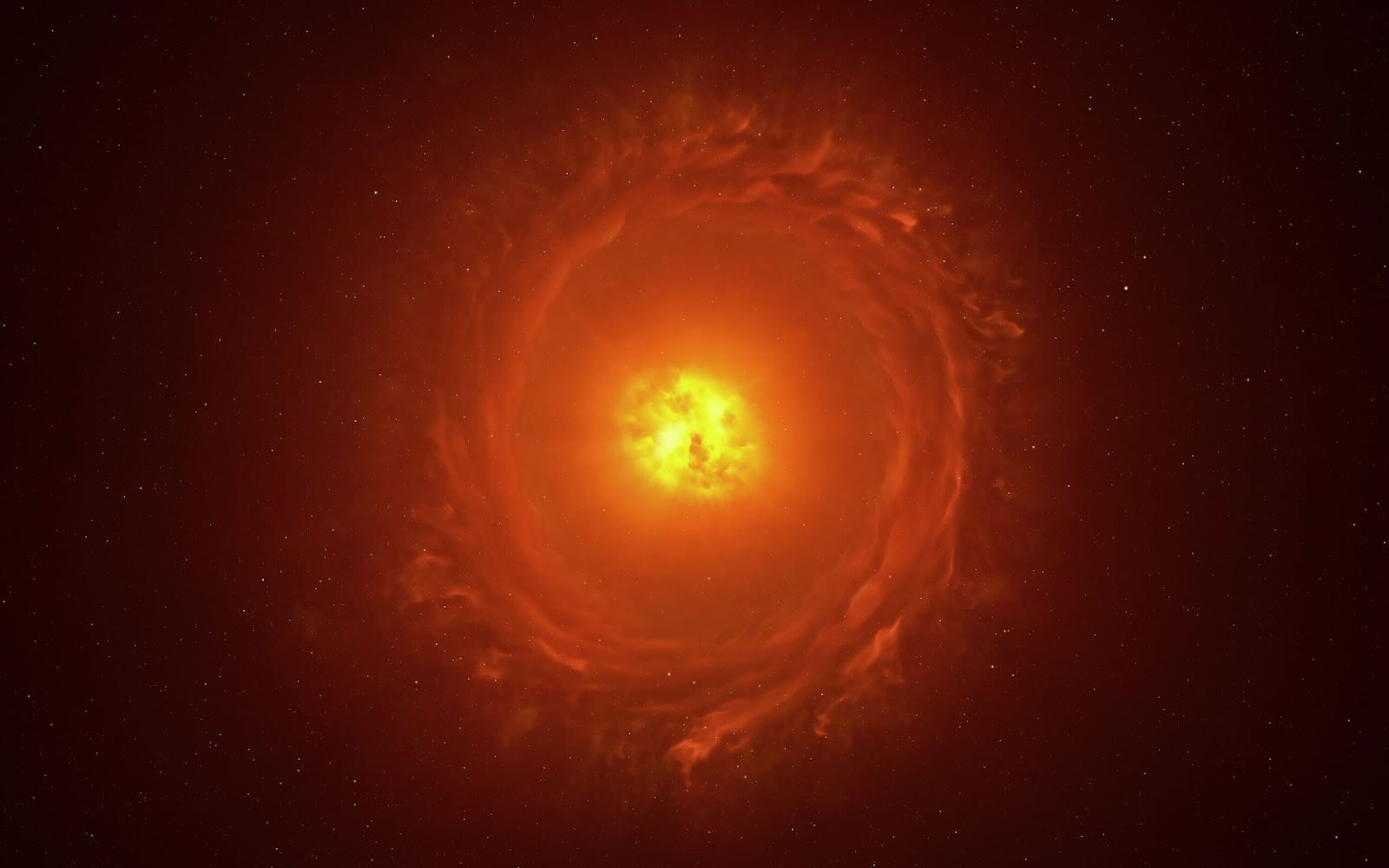

“For a long time, WOH G64 was known as the most extreme red supergiant outside our Galaxy,” said researchers led by Jacco Th. van Loon of Keele University. “However, in a matter of years it has faded” and “its pulsations have become suppressed.”
“We have presented evidence that the remarkable changes witnessed in the 21st-century in the optical brightness and spectrum of the most extreme known extragalactic red supergiant, WOH G64 may be due to binary interaction,” the team continued, noting that “we may be witnessing the birth of a…supernova progenitor.”
Fortunately, this time bomb is located 160,000 light years away, so we are well beyond the blast radius. Whenever WOH G64 does explode, the supernova could be bright enough to see with the naked eye from Earth, despite its location far outside the Milky Way.
Learn with doggo-lingo
It’s not your imagination: Your dog might actually be a really good listener. While it’s well-known that dogs respond to a variety of commands, researchers have now demonstrated that some pooches, known as Gifted Word Learners, can pick up new words just by passively overhearing their owners’ conversations.
Over a series of experiments, researchers gave dogs fun toys to play with, which their owners then named in conversations that were not directed at the dogs. The pets were then able to identify the toys by the labels at a rate significantly above what would be expected by chance, even though they had never been directly taught the words.

The findings suggest that some dogs may have sociocognitive skills parallel to young toddlers, and further confirms that a variety of animals can demonstrate various degrees of language comprehension. But the best part is the following detail about how the effervescent joy of dogs was accounted for in the experimental design.
“Because dogs are neophilic and often get excited by new toys, we gave them ample opportunities to interact with the toys without hearing their labels,” said researchers led by Shany Dror of University of Veterinary Medicine in Vienna.
Science completed? Check. Dogs got loads of playtime? Check. Win-win.
Jellyfish naps > cat naps
We’ll close by yawning and going back to bed—a waterbed in this case, because this is a story about the sleep cycles of marine animals. To probe the broader evolutionary purpose of sleep, scientists monitored periods of slumber and wakefulness in the upside-down jellyfish Cassiopea andromeda and the anemone Nematostella vectensis.
The results revealed that these animals had remarkably similar sleeping habits to people. “Like humans, both species require a total of approximately 8 hours of sleep per day,” said researchers led by Raphaël Aguillon, who conducted the work at Bar-Ilan University, and is now at IBPC Paris-Sorbonne University.
“Notably, similar to findings in primates and flies, a midday nap was also observed in C. andromeda,” the team added.
Talk about sleeping with the fishes! The upshot of the study is that sleep has evolved across all animals with a nervous system to help repair damaged DNA, a benefit that is apparently worth the vulnerability of a resting state. But for our weekend purposes, my takeaway is that even jellyfish enjoy a midday nap, so go ahead and take that siesta.
Thanks for reading! See you next week.

